Human Nervous System:
Question: What are the structural and functional units of the nervous system?
A) Hormones
B) Neurons
C) Photoreceptors
D) Sense organs
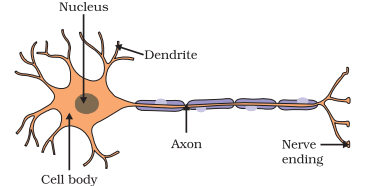
Answer: B) Neurons
Explanation: Neurons or nerve cells are the structural and functional units of the nervous system.
Question: What is the functional junction between neurons called?
A) Synapse
B) Dendrite
C) Axon
D) Nerve impulse
Answer: A) Synapse
Explanation: The functional junction between neurons is called a synapse.
Question: What is the information passing through neurons in the form of?
A) Hormones
B) Electrical signals
C) Chemical signals
D) Photons
Answer: C) Chemical signals
Explanation: Information passing through neurons is in the form of chemical and electrical signals known as nerve impulses.
Question: What part of the neuron carries impulses away from the cell body?
A) Dendrite
B) Synapse
C) Axon
D) Nucleus
Answer: C) Axon
Explanation: The axon conducts impulses away from the cell body.
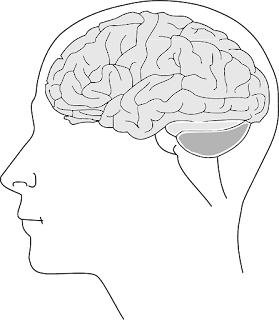
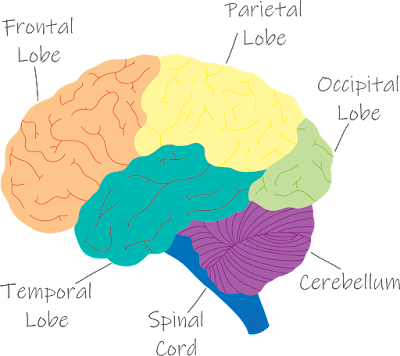
Question: What is the largest part of the human brain?
A) Hindbrain
B) Cerebrum
C) Cerebellum
D) Medulla oblongata
Answer: B) Cerebrum
Explanation: The cerebrum is the most complex and specialized part of the brain.
Hormones:
Question: Who introduced the term "hormones"?
A) Bayliss and Stasling
B) Darwin and Mendel
C) Watson and Crick
D) Curie and Rutherford
Answer: A) Bayliss and Stasling
Explanation: The term "hormones" was introduced by Bayliss and Stasling.
Question: Where are hormones secreted from?
A) Nerve cells
B) Endocrine glands
C) Sense organs
D) Neurons
Answer: B) Endocrine glands
Explanation: Hormones are chemical substances secreted by endocrine glands.
Question: What is the characteristic of hormones?
A) They are secreted by exocrine glands
B) They act on any tissue in the body
C) They are poured directly into the lymphatic system
D) They act on specific target organs
Answer: D) They act on specific target organs
Explanation: Hormones act on specific tissues/organs called target organs.
Question: Which gland regulates the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland?
A) Thyroid
B) Pancreas
C) Hypothalamus
D) Adrenal
Answer: C) Hypothalamus
Explanation: The hypothalamus regulates the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland.
Question: What does the hormone vasopressin regulate?
A) Blood pressure
B) Blood glucose
C) Water and electrolyte balance
D) Muscle contractions
Answer: C) Water and electrolyte balance
Explanation: Vasopressin regulates water and electrolyte balance.
Human Nervous System:
Question: What fluid protects the brain from mechanical shocks?
A) Blood
B) Cerebrospinal fluid
C) Lymph
D) Synaptic fluid
Answer: B) Cerebrospinal fluid
Explanation: The space between the membranes covering the brain is filled by cerebrospinal fluid, which protects the brain from mechanical shocks.
Question: What are the three regions of the human brain?
A) Frontal, parietal, occipital
B) Forebrain, middle brain, hindbrain
C) Cerebrum, cerebellum, medulla oblongata
D) Left hemisphere, right hemisphere, midbrain
Answer: B) Forebrain, middle brain, hindbrain
Explanation: The human brain is broadly divided into three regions: forebrain, middle brain, and hindbrain.
Question: Which part of the brain regulates movements and posture coordination?
A) Cerebrum
B) Medulla oblongata
C) Pons
D) Cerebellum
Answer: D) Cerebellum
Explanation: The cerebellum is responsible for movement and posture coordination.
Question: What is the function of the medulla oblongata?
A) Regulation of respiration
B) Regulation of heartbeat
C) Regulation of digestion
D) Regulation of vision
Answer: A) Regulation of respiration
Explanation: The medulla oblongata regulates functions like swallowing, coughing, sneezing, and respiration.
Question: Which nervous system controls and integrates the functions of internal organs?
A) Central nervous system
B) Peripheral nervous system
C) Autonomic nervous system
D) Somatic nervous system
Answer: C) Autonomic nervous system
Explanation: The autonomic nervous system mainly controls and integrates the functions of internal organs.
Hormones:
Question: What is the role of prolactin?
A) Regulation of blood pressure
B) Regulation of mammary gland function
C) Regulation of metabolism
D) Regulation of bone development
Answer: B) Regulation of mammary gland function
Explanation: Prolactin regulates the function of the mammary gland.
Question: Which hormone is responsible for the regulation of blood calcium and phosphate?
A) Thyroxin
B) Parathyroid hormone
C) Insulin
D) Adrenaline
Answer: B) Parathyroid hormone
Explanation: Parathyroid hormone regulates blood calcium and phosphate levels.
Question: What is the function of oxytocin?
A) Regulation of water balance
B) Stimulation of muscle contractions
C) Regulation of blood glucose
D) Inhibition of bone growth
Answer: B) Stimulation of muscle contractions
Explanation: Oxytocin stimulates contractions of smooth muscles, aiding in childbirth and lactation.
Question: Which hormone is responsible for the regulation of the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins?
A) Adrenalin
B) Thyroxin
C) Insulin
D) Growth hormone
Answer: B) Thyroxin
Explanation: Thyroxin regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
Question: What is the function of insulin?
A) Increasing blood glucose
B) Regulating blood pressure
C) Lowering blood glucose
D) Stimulating muscle contractions
Answer: C) Lowering blood glucose
Explanation: Insulin lowers blood glucose levels.
Human Nervous System:
Question: What can record the electrical activity of the brain?
A) EKG
B) EEG
C) MRI
D) PET scan
Answer: B) EEG (Electro Encephalogram Graphy)
Explanation: EEG can record the electrical activity of the brain.
Question: What is the term for an unconscious and involuntary response of effectors to a stimulus?
A) Reflex action
B) Voluntary action
C) Contraction
D) Inhibition
Answer: A) Reflex action
Explanation: Reflex action is an unconscious and involuntary response to a stimulus.
Question: Which part of the nervous system transmits information from the brain to effector organs?
A) Sensory neurons
B) Motor neurons
C) Interneurons
D) Synaptic neurons
Answer: B) Motor neurons
Explanation: Motor neurons transmit information from the brain to effector organs.
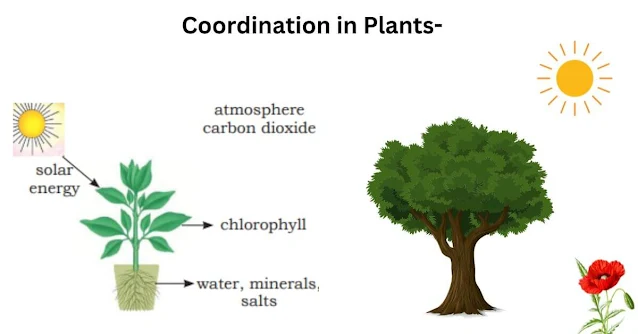
Question: What is the movement of plants in response to a stimulus known as?
A) Reflex
B) Tropism
C) Nastic movement
D) Chemotropism
Answer: B) Tropism
Explanation: The movement of plants in response to a stimulus is known as tropism.
Question: What regulates flowering and seed germination in plants?
A) Phytochrome
B) Auxins
C) Gibberellin
D) Cytokinins
Answer: A) Phytochrome
Explanation: Photoperiodism in plants, including flowering and seed germination, is regulated by the presence of small pigments called phytochrome.
Hormones:
Question: Which hormone is responsible for the regulation of male accessory sex organs and secondary sexual characters?
A) Estrogen
B) Progesterone
C) Testosterone
D) Prolactin
Answer: C) Testosterone
Explanation: Testosterone regulates male accessory sex organs and secondary sexual characters.
Question: What is the role of estrogen and progesterone in females?
A) Regulation of mammary gland function
B) Regulation of water balance
C) Regulation of female accessory sex organs and secondary sexual characters
D) Regulation of blood calcium and phosphate
Answer: C) Regulation of female accessory sex organs and secondary sexual characters
Explanation: Estrogen and progesterone regulate female accessory sex organs and secondary sexual characteristics.
Question: Which gland is responsible for the secretion of growth hormones and tropic hormones?
A) Thyroid
B) Pancreas
C) Adrenal
D) Pituitary gland
Answer: D) Pituitary gland
Explanation: The pituitary gland secretes growth hormones and tropic hormones.
Question: What hormone is released during the "fight or flight" response?
A) Adrenalin
B) Cortisol
C) Insulin
D) Thyroxin
Answer: A) Adrenalin
Explanation: Adrenalin is released during the "fight or flight" response, regulating blood pressure, heart rate, and carbohydrate metabolism.
Question: What is the function of vasopressin?
A) Regulation of metabolism
B) Regulation of water and electrolyte balance
C) Stimulation of muscle contractions
D) Lowering blood glucose
Answer: B) Regulation of water and electrolyte balance
Explanation: Vasopressin regulates water and electrolyte balance.
Human Nervous System:
Question: What is the term for the bending of a growing plant toward unidirectional light?
A) Geotropism
B) Phototropism
C) Chemotropism
D) Nastic movement
Answer: B) Phototropism
Explanation: Phototropism is the movement of a growing plant toward unidirectional light.
Question: Which part of the brain is responsible for receiving information from sense organs?
A) Hindbrain
B) Cerebellum
C) Forebrain
D) Medulla oblongata
Answer: C) Forebrain
Explanation: The forebrain, particularly the cerebrum, has sensory areas where information is received from sense organs.
Question: What type of movement is exhibited by roots growing in response to gravity?
A) Phototropism
B) Chemotropism
C) Geotropism
D) Nastic movement
Answer: C) Geotropism
Explanation: Geotropism is the movement of plant parts in response to gravity.
Question: What is the term for movement in response to a chemical stimulus in plants?
A) Phototropism
B) Chemotropism
C) Geotropism
D) Nastic movement
Answer: B) Chemotropism
Explanation: Chemotropism is movement in response to a chemical stimulus.
Question: What is the term for the movement of plants that is not directed toward or away from a stimulus?
A) Nastic movement
B) Phototropism
C) Geotropism
D) Chemotropism
Answer: A) Nastic movement
Explanation: Nastic movement is a non-directional movement in response to a stimulus.
Hormones:
Question: Which hormone is responsible for the regulation of blood pressure, heart rate, and carbohydrate metabolism?
A) Adrenalin
B) Cortisol
C) Insulin
D) Thyroxin
Answer: A) Adrenalin
Explanation: Adrenalin regulates blood pressure, heart rate, and carbohydrate metabolism.
Question: What hormone is essential for the development of bones and muscles?
A) Prolactin
B) Growth hormone
C) Testosterone
D) Thyroxin
Answer: B) Growth hormone
Explanation: Growth hormone is essential for the development of bones and muscles.
Question: What is the primary function of the hormone insulin?
A) Increasing blood glucose
B) Regulating blood pressure
C) Lowering blood glucose
D) Stimulating muscle contractions
Answer: C) Lowering blood glucose
Explanation: Insulin's primary function is to lower blood glucose levels.
Question: Which gland regulates the secretion of hormones from various endocrine glands?
A) Adrenal
B) Thyroid
C) Pancreas
D) Hypothalamus
Answer: D) Hypothalamus
Explanation: The hypothalamus regulates the secretion of hormones from various endocrine glands.
Question: What is the term for the unconscious withdrawal of hands from a hot surface?
A) Voluntary action
B) Reflex action
C) Involuntary action
D) Nastic movement
Answer: B) Reflex action
Explanation: The unconscious withdrawal of hands from a hot surface is a reflex action.
Human Nervous System:
Question: What is the function of the sense organs in animals?
A) Motor control
B) Hormone secretion
C) Reception of external information
D) Blood circulation
Answer: C) Reception of external information
Explanation: Sense organs in animals are specialized structures for receiving external information.
Question: Which part of the nervous system regulates involuntary functions such as heartbeat and digestion?
A) Central nervous system
B) Peripheral nervous system
C) Autonomic nervous system
D) Somatic nervous system
Answer: C) Autonomic nervous system
Explanation: The autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary functions like heartbeat and digestion.
Question: What is the term for an instrument that records the electrical activity of the brain?
A) Microscope
B) Electrocardiogram
C) Electroencephalogram
D) Stethoscope
Answer: C) Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Explanation: An EEG records the electrical activity of the brain.
Question: Which part of the brain is responsible for the regulation of respiration?
A) Cerebrum
B) Pons
C) Medulla oblongata
D) Cerebellum
Answer: C) Medulla oblongata
Explanation: The medulla oblongata regulates functions like respiration.
Question: What is the term for an unconscious and involuntary response of effectors to a stimulus?
A) Voluntary action
B) Reflex action
C) Involuntary action
D) Nastic movement
Answer: B) Reflex action
Explanation: Reflex action is an unconscious and involuntary response to a stimulus.
Hormones:
Question: What is the function of the hormone vasopressin?
A) Regulation of metabolism
B) Regulation of water and electrolyte balance
C) Stimulation of muscle contractions
D) Lowering blood glucose
Answer: B) Regulation of water and electrolyte balance
Explanation: Vasopressin regulates water and electrolyte balance.
Question: Which hormone is responsible for the development of mammary glands and lactation?
A) Prolactin
B) Oxytocin
C) Thyroxin
D) Estrogen
Answer: A) Prolactin
Explanation: Prolactin is responsible for the development of mammary glands and lactation.
Question: What is the role of the hormone oxytocin?
A) Regulation of water balance
B) Stimulation of muscle contractions and childbirth
C) Regulation of blood calcium
D) Regulation of metabolism
Answer: B) Stimulation of muscle contractions and childbirth
Explanation: Oxytocin stimulates smooth muscle contractions, aiding in childbirth.
Question: Which gland is often referred to as the "master gland" because it regulates other endocrine glands?
A) Thyroid
B) Pituitary gland
C) Adrenal gland
D) Pancreas
Answer: B) Pituitary gland
Explanation: The pituitary gland is often called the "master gland" for its regulatory role.
Question: What hormone is essential for the regulation of blood calcium and phosphate levels?
A) Insulin
B) Parathyroid hormone
C) Adrenaline
D) Growth hormone
Answer: B) Parathyroid hormone
Explanation: Parathyroid hormone regulates blood calcium and phosphate levels.
What are the two types of control and coordination?
There are two types of co-ordinations i.e., nervous and hormonal co-ordination.
What are the two principles of coordination?
Continuity:- It is the most important principle of coordination. Because it is a continuous process and cannot be left or restricted to some activities. The entire organization requires coordination around the clock. Reciprocal Relationship:- It is the best principle of effective coordination.
What are the main components of coordination?
Coordinated movement is characterized by appropriate speed, distance, direction, timing and muscular tension.



.jpg)
.png)
.png)
.png)







If you have any doubts please comment