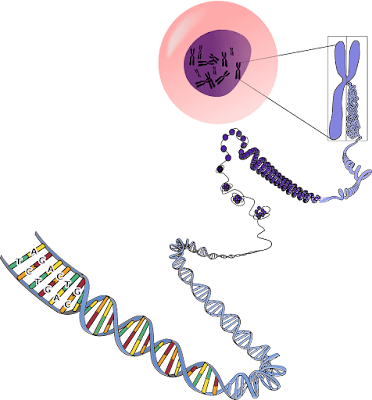
DNA is the basic thread that weaves the genetic information necessary for the development, operation, growth, and reproduction of all known species in the complex tapestry of life. This amazing molecule has fascinated scientists and enthusiasts for decades. It is made up of two polynucleotide chains that form a double helix. We set out on a voyage of discovery using MCQS On DNA Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) that solve the secrets of this fundamental macromolecule in order to explore deeper into the intriguing world of DNA.
MCQS On DNA.
1. What does DNA stand for?
a. Deoxyribonucleic Acid
b. Ribonucleic Acid
c. Deoxynucleotide Assembly
d. Ribonucleotide Adenosine
Answer: a. Deoxyribonucleic Acid
Explanation: DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid.
2. How many polynucleotide chains make up the structure of DNA?
a. One
b. Two
c. Three
d. Four
Answer: b. Two
Explanation: DNA is composed of two polynucleotide chains that coil around each other.
3. What are the building blocks of DNA called?
a. Amino Acids
b. Nucleotides
c. Monomers
d. Carbohydrates
Answer: b. Nucleotides
Explanation: DNA is made up of repeating units called nucleotides.
4. What are the nitrogenous bases in DNA?
a. A, C, G, U
b. A, C, G, T
c. A, U, G, T
d. A, T, C, P
Answer: b. A, C, G, T
Explanation: The nitrogenous bases in DNA are Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), and Thymine (T).
5. How are the two strands of DNA held together?
a. Ionic Bonds
b. Covalent Bonds
c. Hydrogen Bonds
d. Peptide Bonds
Answer: c. Hydrogen Bonds
Explanation: The nitrogenous bases of the two DNA strands are held together by hydrogen bonds.
6. What is the role of DNA in organisms?
a. Energy storage
b. Structural support
c. Genetic instructions
d. Enzyme activation
Answer: c. Genetic instructions
Explanation: DNA carries genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of organisms.
7. Which nucleotide is complementary to Adenine in DNA?
a. Thymine
b. Cytosine
c. Guanine
d. Uracil
Answer: a. Thymine
Explanation: Adenine pairs with Thymine in DNA.
8. What is the process of creating RNA from DNA called?
a. Translation
b. Transcription
c. Replication
d. Reverse Transcription
Answer: b. Transcription
Explanation: RNA strands are created using DNA strands as a template in the process of transcription.
9. Where is DNA primarily located in eukaryotic cells?
a. Cytoplasm
b. Nucleus
c. Mitochondria
d. Chloroplasts
Answer: b. Nucleus
Explanation: In eukaryotic cells, DNA is primarily located inside the cell nucleus.
10. What is the sugar in DNA called?
a. Glucose
b. Ribose
c. Deoxyribose
d. Fructose
Answer: c. Deoxyribose
- Explanation: The sugar in DNA is deoxyribose.
11. What is the term for the process of DNA duplication before cell division?
a. Translation
b. Replication
c. Transcription
d. Mitosis
Answer: b. Replication
- Explanation: DNA undergoes replication before cell division to produce identical copies.
12. In DNA replication, what enzyme is responsible for synthesizing the new DNA strand?
a. RNA Polymerase
b. Ligase
c. Helicase
d. DNA Polymerase
Answer: d. DNA Polymerase
- Explanation: DNA Polymerase is the enzyme responsible for synthesizing the new DNA strand during replication.
13. What is the term for the coiling of DNA into tight loops and other shapes?
a. Replication
b. Transcription
c. Translation
d. DNA Packaging
Answer: d. DNA Packaging
- Explanation: The structure of DNA is dynamic, capable of coiling into tight loops and other shapes, known as DNA packaging.
14. What is the name of the structures that organize DNA within eukaryotic chromosomes?
a. Nucleosomes
b. Ribosomes
c. Centrioles
d. Golgi Apparatus
Answer: a. Nucleosomes
- Explanation: Chromatin proteins, such as histones, organize DNA into structures called nucleosomes.
15. Which of the following is a pyrimidine base in DNA?
a. Adenine (A)
b. Guanine (G)
c. Cytosine (C)
d. Thymine (T)
Answer: c. Cytosine (C)
- Explanation: Cytosine is a pyrimidine base in DNA.
16. What type of bonds primarily stabilize the DNA double helix?
a. Ionic Bonds
b. Covalent Bonds
c. Hydrogen Bonds
d. Peptide Bonds
Answer: c. Hydrogen Bonds
- Explanation: The DNA double helix is primarily stabilized by hydrogen bonds between nucleotides.
17. Which nucleotide is present in RNA but not in DNA?
a. Adenine (A)
b. Cytosine (C)
c. Guanine (G)
d. Uracil (U)
Answer: d. Uracil (U)
- Explanation: RNA contains Uracil (U) instead of Thymine (T) found in DNA.
18. What is the term for the end of a DNA strand with a free hydroxyl group attached to the 3′ carbon?
a. 3' Phosphoryl
b. 5' Phosphoryl
c. 3' Hydroxyl
d. 5' Hydroxyl
Answer: c. 3' Hydroxyl
- Explanation: The 3' end of a DNA strand has a terminal hydroxyl group.
19. In a nucleic acid double helix, how do the orientations of the nucleotides in one strand compare to the other strand?
a. Parallel
b. Antiparallel
c. Perpendicular
d. Diagonal
Answer: b. Antiparallel
- Explanation: The strands in a DNA double helix run in opposite directions, making them antiparallel.
20. What is the major difference in the sugar between DNA and RNA?
a. Deoxyribose in DNA, Ribose in RNA
b. Ribose in DNA, Deoxyribose in RNA
c. Glucose in DNA, Fructose in RNA
d. Sucrose in DNA, Maltose in RNA
Answer: a. Deoxyribose in DNA, Ribose in RNA
- Explanation: DNA contains deoxyribose, while RNA contains ribose as their respective sugars.
21. What is the function of DNA polymerase in DNA replication?
a. Unzipping the DNA double helix
b. Synthesizing RNA primers
c. Synthesizing a new DNA strand
d. Breaking hydrogen bonds between nucleotides
Answer: c. Synthesizing a new DNA strand
- Explanation: DNA polymerase is responsible for synthesizing a new DNA strand during DNA replication.
22. Which base pairs with Guanine in DNA?
a. Adenine
b. Cytosine
c. Thymine
d. Uracil
Answer: b. Cytosine
- Explanation: Guanine pairs with Cytosine in DNA.
23. Where is most of the DNA stored in prokaryotic cells?
a. Nucleus
b. Cytoplasm
c. Mitochondria
d. Chloroplasts
Answer: b. Cytoplasm
- Explanation: Prokaryotic cells store their DNA in the cytoplasm.
24. What is the purpose of DNA transcription?
a. Synthesizing a new DNA strand
b. Synthesizing RNA from DNA
c. Breaking down DNA into nucleotides
d. Replicating the entire genome
Answer: b. Synthesizing RNA from DNA
- Explanation: DNA transcription is the process of synthesizing RNA from a DNA template.
25. What is the name of the process where DNA information is used to create proteins?
a. Replication
b. Transcription
c. Translation
d. Codification
Answer: c. Translation
- Explanation: Translation is the process where RNA information is used to create proteins.
26. Which DNA structure has an exposed 5' phosphate on one strand and an exposed 3′ hydroxyl group on the other?
a. A nucleotide
b. A DNA double helix
c. A nucleoside
d. A phosphodiester bond
Answer: d. A phosphodiester bond
- Explanation: The ends of a DNA strand have a 5' phosphate and a 3' hydroxyl group, forming a phosphodiester bond.
27. What is the buoyant density of most DNA?
a. 1.0 g/cm³
b. 1.7 g/cm³
c. 2.0 g/cm³
d. 2.5 g/cm³
Answer: b. 1.7 g/cm³
- Explanation: The buoyant density of most DNA is 1.7 g/cm³.
28. What type of sugar is found in RNA?
a. Deoxyribose
b. Ribose
c. Glucose
d. Maltose
Answer: b. Ribose
- Explanation: RNA contains ribose as its sugar.
29. What are the two forces that primarily stabilize the DNA double helix?
a. Ionic bonds and covalent bonds
b. Hydrogen bonds and covalent bonds
c. Peptide bonds and hydrogen bonds
d. Ionic bonds and hydrogen bonds
Answer: b. Hydrogen bonds and covalent bonds**
- Explanation: Hydrogen bonds and covalent bonds primarily stabilize the DNA double helix.
30. What term is used for the process where DNA is organized into long structures called chromosomes before cell division?
a. Replication
b. Transcription
c. Packaging
d. Condensation
Answer: c. Packaging
- Explanation: DNA is organized into chromosomes through a process known as packaging before cell division.
31. What is the term for the sequence of amino acids within proteins specified by RNA strands during translation?
a. Replication
b. Codification
c. Transcription
d. Translation
Answer: b. Codification
- Explanation: The sequence of amino acids within proteins is specified by RNA strands during translation.
32. What is the main difference between the sugar in DNA and RNA?
a. The number of carbon atoms
b. The presence of oxygen
c. The type of bonds it forms
d. The absence of phosphate groups
Answer: a. The number of carbon atoms
- Explanation: DNA has deoxyribose with five carbon atoms, while RNA has ribose with five carbon atoms.
33. Which of the following is a purine base in DNA?
a. Adenine (A)
b. Thymine (T)
c. Cytosine (C)
d. Uracil (U)
Answer: a. Adenine (A)
- Explanation: Adenine is a purine base in DNA.
34. What is the name of the process where DNA information is duplicated before cell division?
a. Replication
b. Transcription
c. Translation
d. Codonization
Answer: a. Replication
- Explanation: DNA replication is the process of duplicating DNA before cell division.
35. In eukaryotic cells, where is mitochondrial DNA primarily located?
a. Nucleus
b. Cytoplasm
c. Mitochondria
d. Chloroplasts
Answer: c. Mitochondria
- Explanation: Mitochondrial DNA is primarily located in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells.
36. What is the term for the pentose sugar found in RNA?
a. Ribose
b. Deoxyribose
c. Glucose
d. Fructose
Answer: a. Ribose
- Explanation: The pentose sugar found in RNA is ribose.
37. What does the term "antiparallel" mean in the context of DNA strands?
a. Running in the same direction
b. Running in opposite directions
c. Coiling into loops
d. Separating during replication
Answer: b. Running in opposite directions
- Explanation: Antiparallel refers to the opposite directions in which the two DNA strands run.
38. What is the purpose of DNA packaging in eukaryotic chromosomes?
a. Facilitate transcription
b. Promote translation
c. Protect DNA from damage
d. Assist in replication
Answer: a. Facilitate transcription
- Explanation: DNA packaging helps organize DNA and guide interactions during transcription.
39. Which enzyme is responsible for unwinding the DNA double helix during DNA replication?
a. DNA Polymerase
b. Helicase
c. Ligase
d. RNA Polymerase
Answer: b. Helicase
- Explanation: Helicase is responsible for unwinding the DNA double helix during replication.
40. What is the name of the structure formed when DNA coils into a double helix?
a. Nucleosome
b. Chromosome
c. Helixosome
d. Nucleotide
Answer: b. Chromosome
- Explanation: The double helix structure of DNA contributes to the formation of chromosomes.
41. Which of the following is a function of DNA that is non-coding?
a. Protein synthesis
b. Energy production
c. Structural support
d. Storage of genetic information
Answer: a. Protein synthesis
- Explanation: Non-coding DNA does not serve as a pattern for protein sequences.
42. What is the name of the process where RNA is synthesized from DNA?
a. Replication
b. Translation
c. Transcription
d. Codonization
Answer: c. Transcription
- Explanation: Transcription is the process of synthesizing RNA from DNA.
43. What is the complementary RNA sequence for the DNA sequence: TACGGA?
a. AUGCCU
b. ATGCCU
c. AUGCCA
d. TACGGA
Answer: a. AUGCCU
- Explanation: RNA substitutes Uracil (U) for Thymine (T), so the complementary RNA sequence is AUGCCU.
44. Which of the following is NOT a nitrogenous base in DNA?
a. Adenine (A)
b. Cytosine (C)
c. Uracil (U)
d. Thymine (T)
Answer: c. Uracil (U)
- Explanation: Uracil is a nitrogenous base in RNA, not DNA.
45. What is the term for the end of a DNA strand with a terminal phosphate group attached to the 5′ carbon?
a. 3' Phosphoryl
b. 5' Phosphoryl
c. 3' Hydroxyl
d. 5' Hydroxyl
Answer: b. 5' Phosphoryl
- Explanation: The 5' end of a DNA strand has a terminal phosphate group.
46. What are the two types of nucleic acids mentioned in the passage?
a. Proteins and lipids
b. DNA and RNA
c. Sugars and carbohydrates
d. Enzymes and hormones
Answer: b. DNA and RNA
- Explanation: DNA and RNA are the two types of nucleic acids.
47. What is the term for the alternating sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA?
a. Helix backbone
b. Nucleotide backbone
c. Phosphodiester linkage
d. Sugar-phosphate linkage
Answer: c. Phosphodiester linkage**
- Explanation: The backbone of DNA is composed of alternating sugar and phosphate groups linked by phosphodiester bonds.
48. What is the structure of DNA known as when it coils into tight loops and shapes?
a. Double helix
b. Nucleosome
c. Chromosome
d. Helicase
Answer: b. Nucleosome
- Explanation: DNA can coil into nucleosomes, which are tight loops formed by chromatin proteins.
49. Which DNA strand serves as the template for RNA synthesis during transcription?
a. Both strands
b. Leading strand
c. Lagging strand
d. Non-coding strand
Answer: a. Both strands**
- Explanation: Both strands of DNA can serve as templates for RNA synthesis during transcription.
50. In the genetic code, what does RNA specify during translation?
a. DNA sequences
b. Amino acid sequences
c. Phosphodiester linkages
d. Nucleotide sequences
Answer: b. Amino acid sequences
- Explanation: RNA strands specify the sequence of amino acids within proteins during translation
Through the use of MCQS On DNA Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs), we have been able to delve deeply into the complex realm of DNA, the molecule that is the foundation of life. Each new inquiry has contributed to the growing body of knowledge on nucleotides and nitrogenous bases, as well as the intricate procedures of transcription, translation, and replication.



.jpg)
.png)
.jpg)






If you have any doubts please comment